What is cirrhosis and how is it related to MASH?
Cirrhosis is the most severe form of scarring of the liver
 This is a model, not a real patient
This is a model, not a real patient
About cirrhosis
Cirrhosis develops over time as liver damage, caused by MASH (formerly known as NASH) or other factors, leads to formation of scar tissue. This scarring impairs the liver's ability to function properly.
Even with cirrhosis, the liver may continue to work for some time. However, cirrhosis can ultimately lead to liver failure and severe complications1, which can be life-threatening.
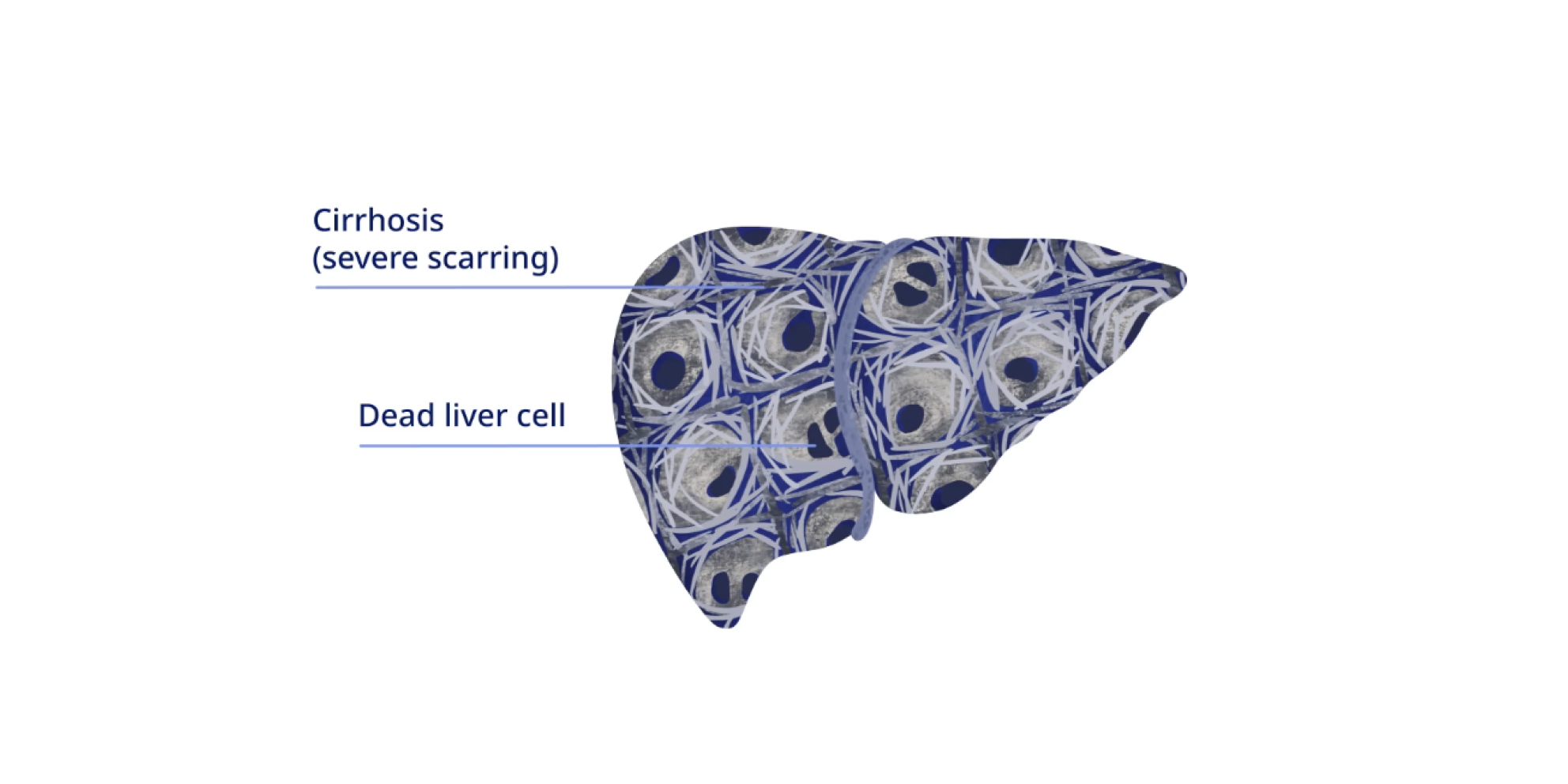 Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
What causes cirrhosis of the liver?
Cirrhosis is a stage of permanent liver damage. One cause of cirrhosis is untreated MASH, which can lead to scarring of the liver (fibrosis). Fibrosis ranges from mild to advanced, with the most severe form being cirrhosis.
Other causes include:
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Viral infections (e.g. Hepatitis B and C)
- Chronic heart failure
Symptoms of cirrhosis2:
At the cirrhosis stage, the liver is no longer functioning properly, leading to noticeable symptoms.
- Fatigue and weakness
- Easy bruising and bleeding
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Itchy skin
- Swelling in the legs, feet, or ankles (edema)
- Abdominal swelling (ascites)
- Spider-like blood vessels on the skin (spider angiomas)
- Red patches on the palms of the hands
- Confusion, drowsiness, and slurred speech (hepatic encephalopathy)
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Weight and muscle loss
- Vomiting blood
- Dark urine and tarry stools
- Swollen legs or abdomen
- Portal hypertension
Symptoms of cirrhosis can often be challenging to recognize and self-diagnose. Seek professional advice from your healthcare provider if you are at risk of MASH or suspect you are showing symptoms.
Cirrhosis treatment
If you are living with MASH, your healthcare provider will likely suggest lifestyle changes (including a balanced diet and an active lifestyle) to help slow the progression of scarring (fibrosis).
However, if you reach cirrhosis, which is the most advanced stage of scarring (fibrosis), the most common treatment is liver transplant surgery3.
MASH and MASLD are updated terms for conditions previously known as NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis) and NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease). Similarly, "steatotic liver disease" is the current term for what was once called "fatty liver disease".
- Cornelius Engelmann, Mechanisms of immunity in acutely decompensated cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/liv.15644 Last accessed: October 2024
- NIH, Symptoms & Causes of Cirrhosis: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/cirrhosis/symptoms-causes Last accessed: August 2024
- Sara Battistella, Liver transplantation for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: indications and post-transplant management: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10029965/ Last accessed: August 2024



